Free Genetic Code revision notes for OCR A Level Biology – covering specification point 2.1.3(f).
The Nature of the Genetic Code
Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins (and some code for RNA).
The order of bases in a gene determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
These bases are read in groups of three; this is known as the triplet code, and each group of three bases forms a codon.
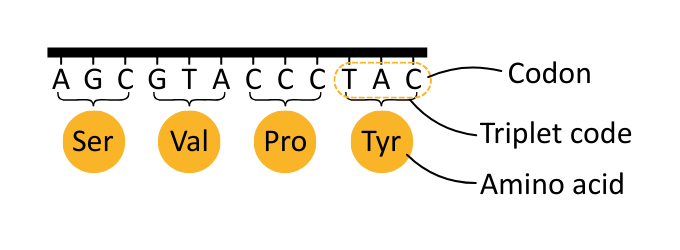
The key features of the triplet genetic code are that it is degenerate, non-overlapping, and universal.
| Property | Description | Biological Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Degenerate | 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. |
Most amino acids have multiple codons. Reduces the impact of point mutations. |
| Non-overlapping | Bases are read in triplets (codons), each base used once. | Each base affects only one amino acid. |
| Universal | The same codons specify the same amino acids in almost all organisms. | Evidence for a common evolutionary ancestor. |