Free Colorimetry revision notes for OCR A Level Biology – covering specification point 2.1.2(r).
Colorimetry
Colorimetry is a quantitative method used to determine the concentration of a coloured solution by measuring how much light is absorbed (or transmitted) through a solution.
A colorimeter measures how much light (of a specific wavelength) passes through a solution placed in a cuvette.
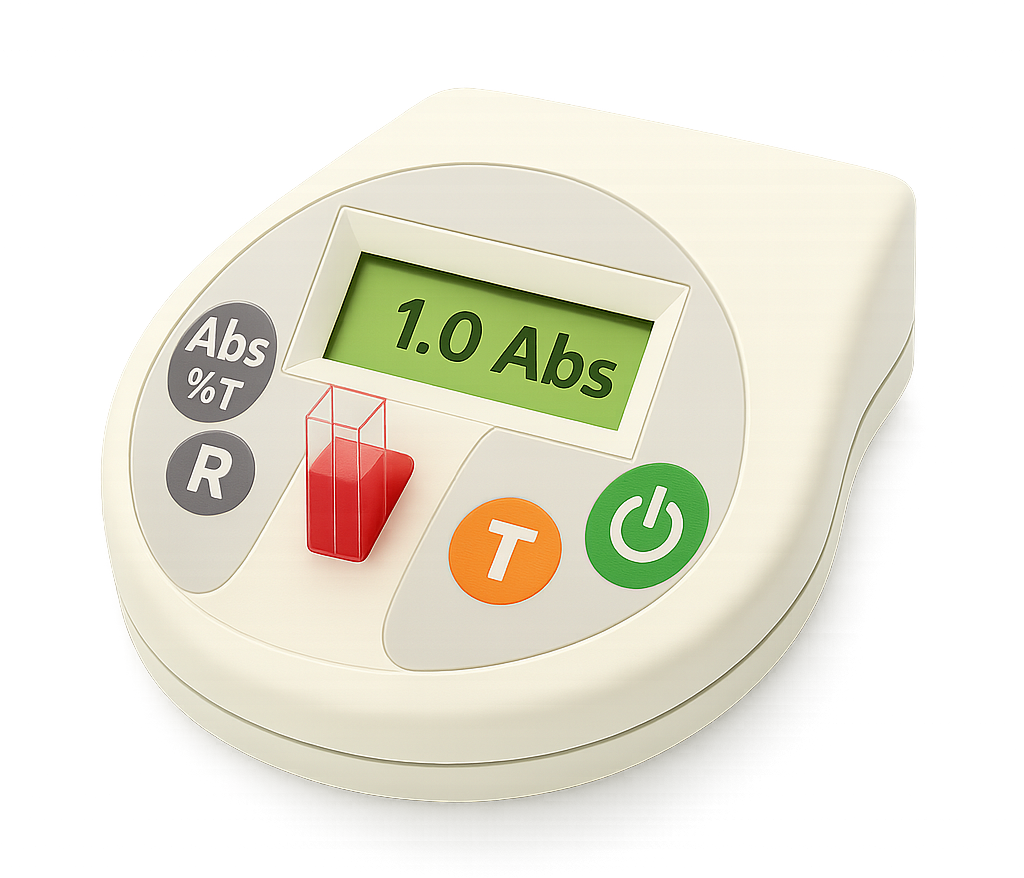
A blank (usually distilled water) is used to calibrate the colorimeter to zero absorbance (or 100% transmission) for comparison with the solution being tested.
Colorimetry for reducing sugars
Procedure:
- Add excess Benedict’s reagent to your sample and heat it to 80oC.
The more reducing sugar present, the more precipitate that forms, and the fewer copper(II) ions remain in solution.
- Centrifuge the mixture to remove the precipitate.
- Collect the supernatant (the clear liquid) and place into a cuvette.
- Calibrate a colorimeter with distilled water (for comparison).
- Use a colorimeter to measure the absorbance of the supernatant.
Use a red filter (blue Benedict’s solution absorbs red light).
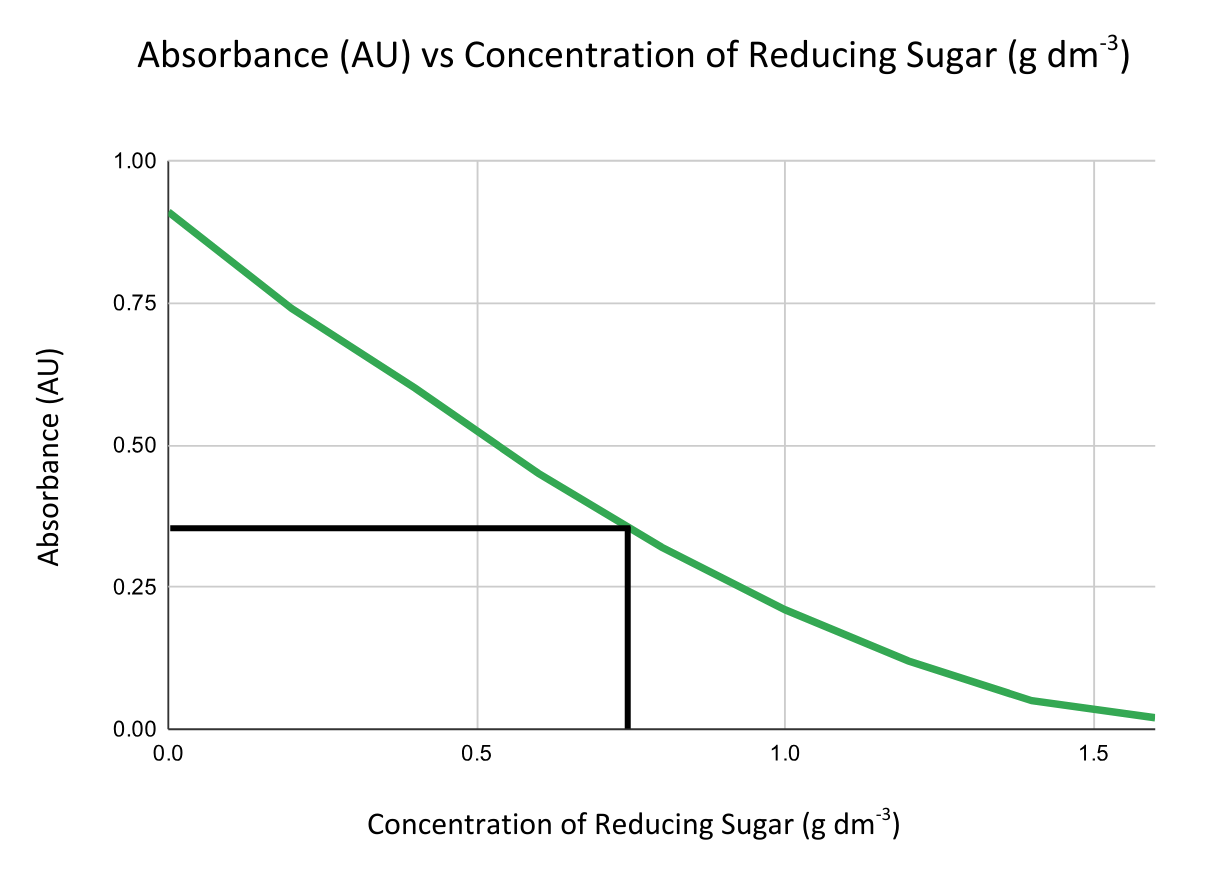
- Compare absorbance readings to those from solutions of known concentration to create a calibration curve by plotting absorbance vs concentration.
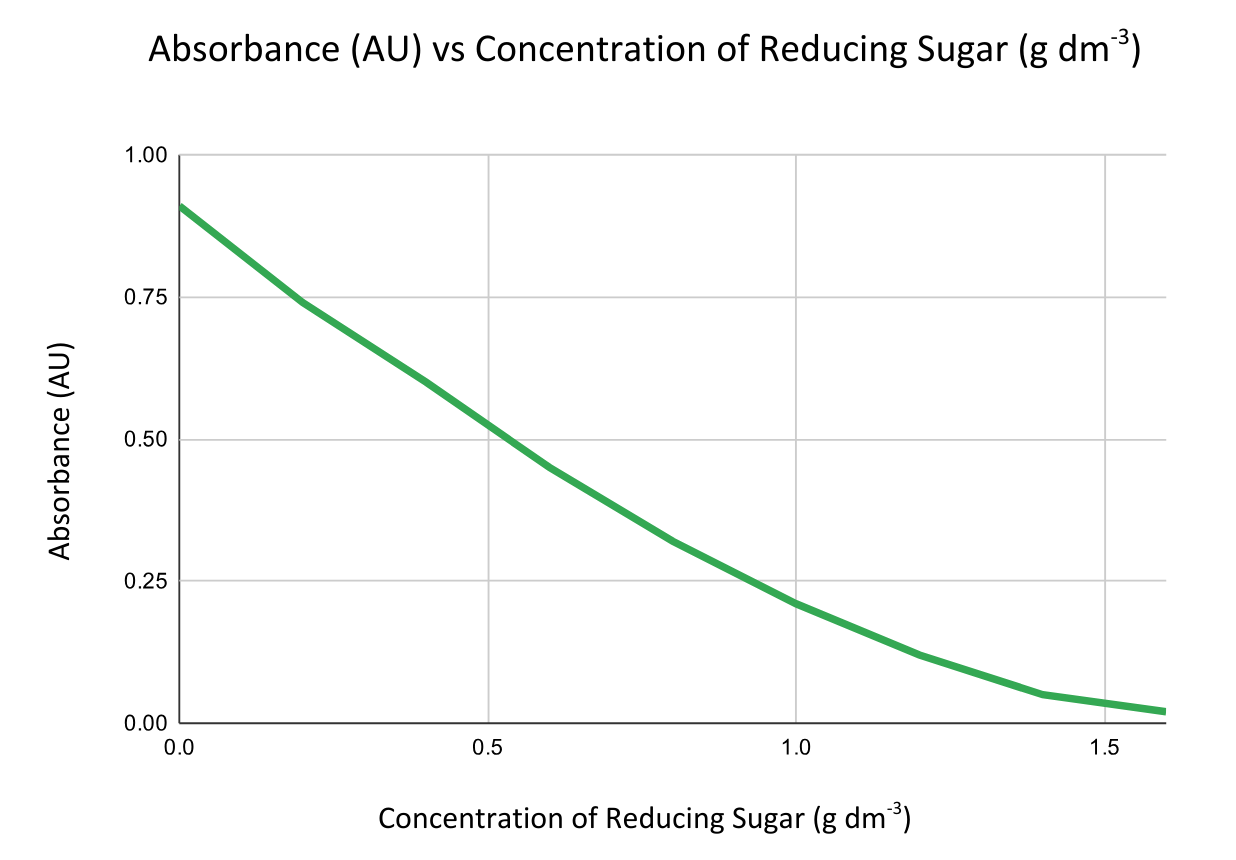
Less absorbance = higher concentration of reducing sugar.
Then use the graph to find the concentration of unknown samples by interpolation.