Module 3: Plant Vascular Systems
These free OCR A Level Biology Plant Vascular Systems revision notes have been written for specification points 3.1.3(b.i) and 3.1.3(b.ii).
Vascular Systems In Plants
The vascular bundle is a collection of xylem and phloem tissue:
- Xylem transports water and dissolved mineral ions from the roots to the leaves (only up) using mass flow.
- Phloem transports organic solutes such as sucrose, amino acids, and hormones (dissolved as phloem sap) throughout the plant (up and down) using translocation.
Xylem Tissue
The table below outlines the structural features of xylem tissue and its benefits:
| Structural Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dead hollow cells | Allow an uninterrupted flow of water from the root to the leaf through a continuous column |
| Vessels with no end walls | Create a continuous tube for mass flow |
| Lignin rings/spirals in cell walls | Lignification strengthens cell walls to provide mechanical support to the xylem (resisting collapse under tension) and to support the plant |
| Bordered pits | Gaps in the lignified xylem vessels that allow water to move from one xylem to another, or into surrounding tissue |
| Narrow lumen | Enables capillary action to support water cohesion, stopping the water column from breaking |
Phloem Tissue
The table below outlines the structural features of phloem tissues and it’s benefits:
| Structural Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sieve tube elements | Long, thin (living) cells with sieve plates at their ends for the passage of phloem sap form tubes end to end |
| Sieve plates |
– Specialised cellulose cell walls with perforations to allow phloem sap from one sieve tube element to another – In the event of injury or infection, the perforations are blocked with callose |
| No nucleus or organelles | Maximises space for phloem sap |
| Companion cells |
– Contain many mitochondria to provide ATP for the active loading of sucrose into sieve tubes for translocation – Carry out metabolic functions for the sieve tube elements |
| Plasmodesmata | Connects sieve tube elements and companion cells, enables hormonal communication and the transport of substances |
Vascular Tissue Arrangement
Vascular tissue is arranged differently in different plant organs, which can be used to identify them.
The table below describes the arrangement of vascular tissue in different plant organs:
| Organ | Vascular Tissue Arrangement | Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| Root | Xylem is in an X-shape at the centre with phloem between the arms. |  |
| Stem | Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring near the outer edge, with xylem on the inner side and phloem on the outer side. | 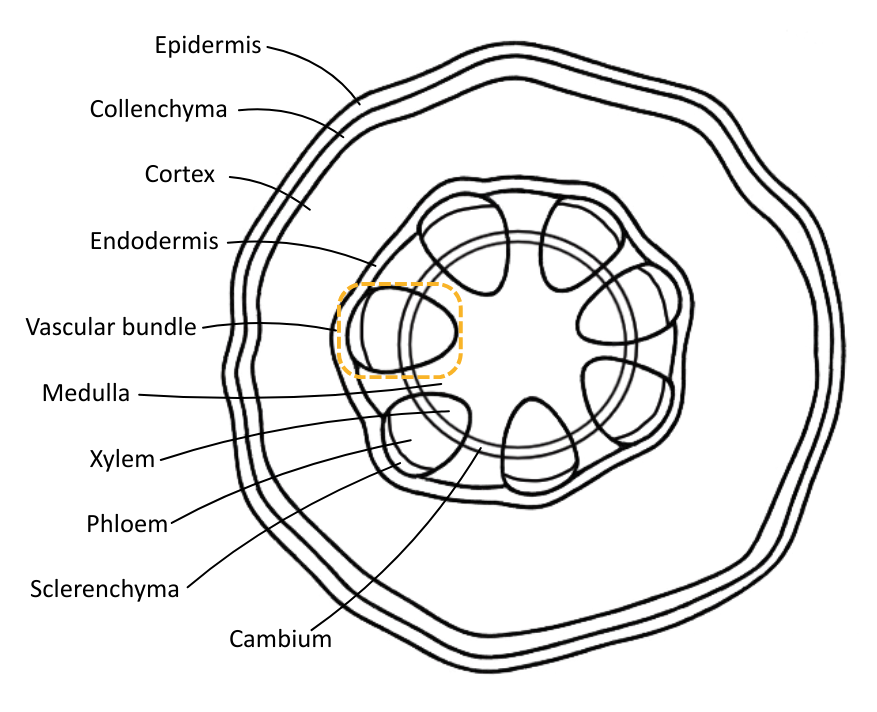 |
| Leaf | Vascular tissue in the midrib and veins, with xylem above and phloem below in the bundle sheath. | 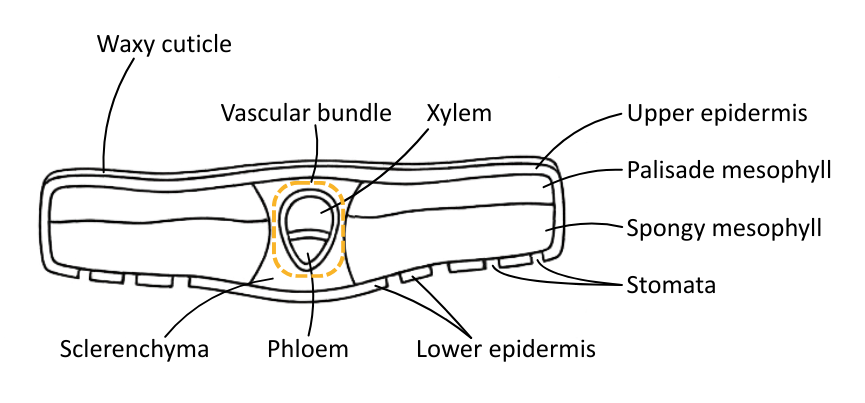 |
