Module 3: Mammalian Gaseous Exchange System
These free OCR A Level Biology Mammalian Gaseous Exchange System revision notes have been written for specification points 3.1.1(a), 3.1.1(b), 3.1.1(c) and 3.1.1(f).
Gaseous Exchange
For the effective exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, mammals have a highly specialised gaseous exchange system consisting of a series of airways that filter, warm, and moisten air before it reaches the alveoli.
The pathway that air follows during inhalation is:
Nasal cavity → Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli
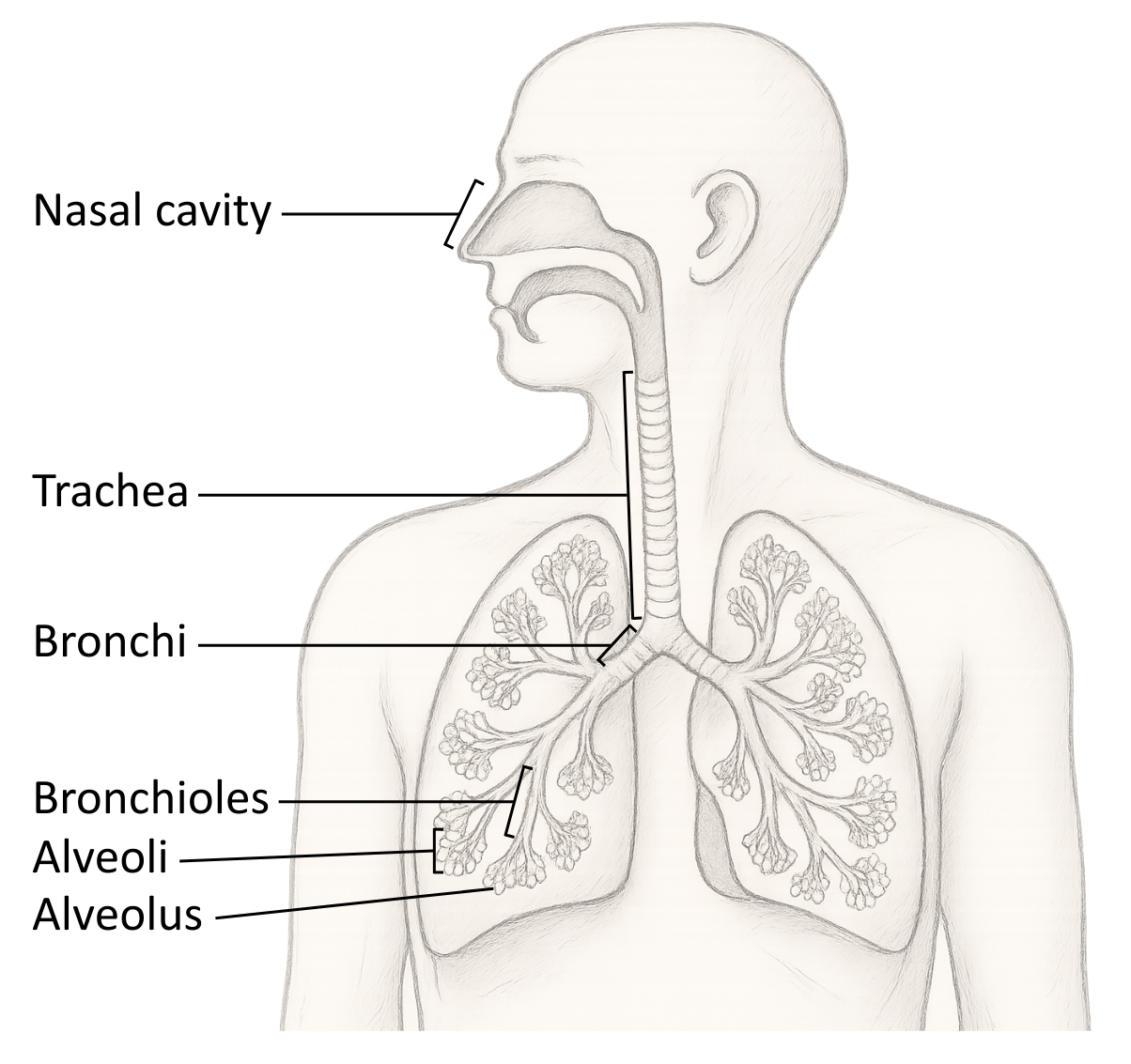
The table below provides an overview of some functions and features of these structures:
| Part | Structure | Function(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Trachea |
– Single-wide tube supported by C-shaped cartilage rings. – Lined with ciliated epithelium and goblet cells. – Contains smooth muscle and elastic fibres. |
– Cartilage prevents the collapse of the airway. – Cilia and mucus trap and remove debris. – Smooth muscle regulates airway diameter. – Elastic fibres recoil after stretching. |
| Bronchi |
– Two tubes branching from the trachea into each lung. – Supported by cartilage plates. – Lined with ciliated epithelium and goblet cells. – Contains smooth muscle and elastic fibres. |
– Cartilage prevents airway collapse. – Cilia and mucus trap and remove debris and microorganisms. – Smooth muscle controls airway diameter. – Elastic fibres provide recoil after stretching. |
| Bronchioles |
– Narrower tubes containing smooth muscle and elastic fibres. – Ciliated epithelium and goblet cells are present in larger bronchioles. |
– Elastic fibres help keep airways open and allow recoil after stretching. – Cilia and mucus trap and remove debris and microorganisms. |
| Alveoli |
– Large surface area with an extensive capillary network. – Short diffusion distance (~0.5 μm). – Microscopic air sacs with squamous epithelium and many elastic fibres. |
– Main site of gas exchange. – Elastic fibres allow recoil to expel air during exhalation. |
