Module 2: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
These free OCR A Level Biology Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids revision notes have been written for specification points 2.1.3(a), 2.1.3(b) and 2.1.3(d.i).
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are DNA and RNA, polymers involved in the encoding and transmission of information in biological life.
Nucleic acids are made up of many nucleotide monomers joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
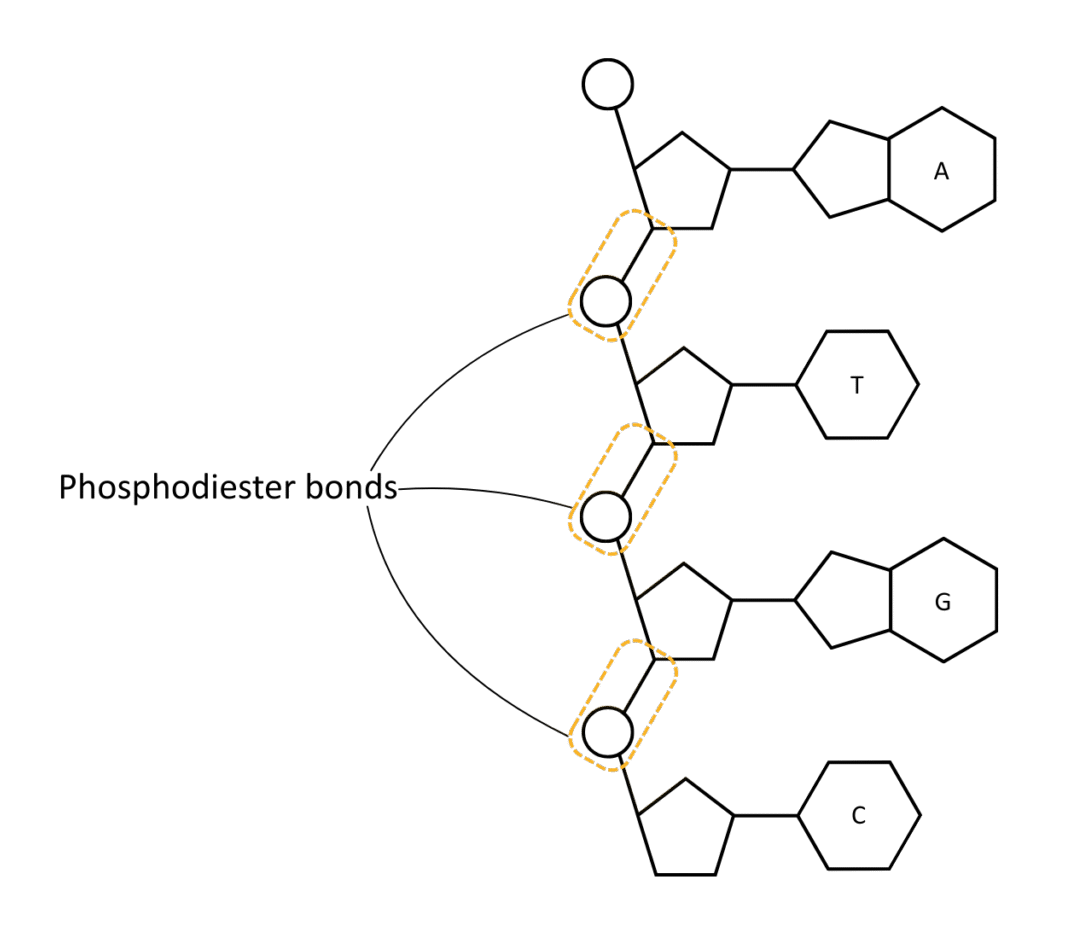
Nucleotides
Nucleotides consist of three components:
- A phosphate group
- A pentose sugar: Deoxyribose (in DNA) or ribose (in RNA)
- A nitrogenous base: Adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, uracil (in RNA)
The image below shows the 4 DNA nucleotides:
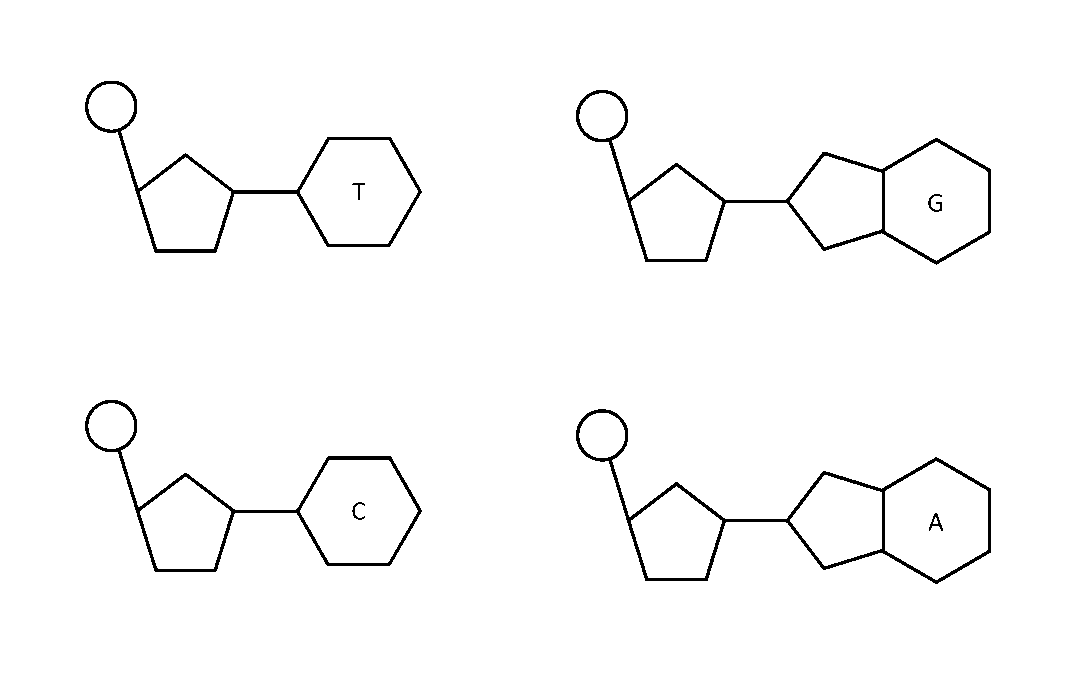
There are two types of nitrogenous bases: purines and pyrimidines.
| Purines | Pyrimidines | |
|---|---|---|
| Bases | Adenine (A), Guanine (G) | Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U)* |
| Structure | Double-ring | Single-ring |
*Uracil is only found in RNA, replacing the use of Thymine.
Phosphodiester Bonds
Phosphodiester bonds form in condensation reactions, where a molecule of water is lost, joining nucleotide monomers together to form nucleic acid polymers.
Phosphodiester bonds are broken in hydrolysis reactions (e.g., during digestion or replication) by using water, breaking nucleic acids back down into their nucleotide monomers.
Nucleotides and DNA Structure
Nucleotides form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA double helix and in RNA.
The DNA double helix is formed when two DNA strands are joined together by hydrogen bonds between their nitrogenous bases.
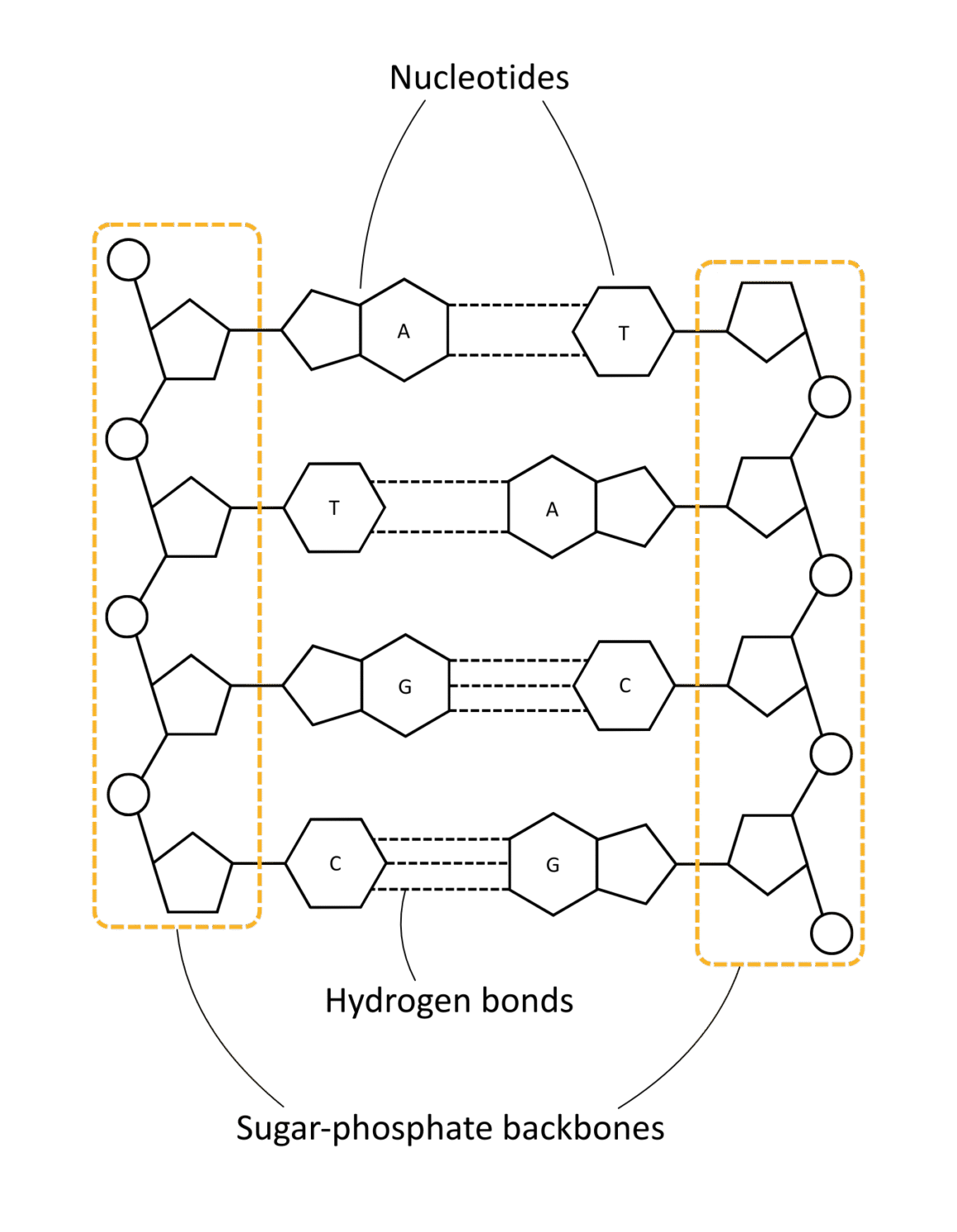
The table below compares and outlines DNA and RNA:
| DNA | RNA | |
|---|---|---|
| Full name | Deoxyribonucleic acid | Ribonucleic acid |
| Strands | Double-stranded | Single-stranded |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | A, T, C, G | A, U, C, G |
| Function | Stores genetic information | Transfers and translates genetic information |
| Structure | Long, double helix | Shorter, varies in shape |
| Base pairing | A–T (2 H bonds) C–G (3 H bonds) | A–U (2 H bonds) C–G (3 H bonds) |
| Location | Nucleus (some in mitochondria and chloroplast) | Made in nucleus, functions in cytoplasm |
| Polymer | Yes | Yes |
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Nucleotides also form ADP and ATP when they are phosphorylated.
ATP → ADP + Pi + energy
This releases energy, which is used for active transport, muscle contraction, metabolic reactions, and more.
