Module 2: Genetic Code
These free OCR A Level Biology Genetic Code revision notes have been written for specification points 2.1.3(f).
The Nature of the Genetic Code
Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins (and some code for RNA).
The order of bases in a gene determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide.
These bases are read in groups of three; this is known as the triplet code, and each group of three bases forms a codon.
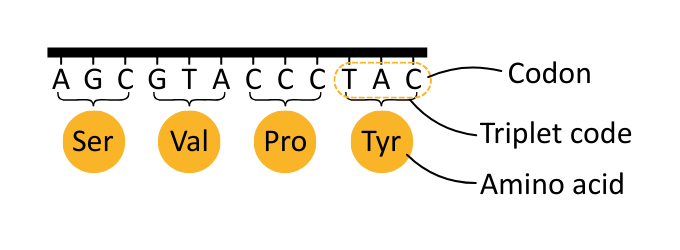
The key features of the triplet genetic code are that it is degenerate, non-overlapping, and universal.
| Property | Description | Biological Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Degenerate | 64 codons but only 20 amino acids. |
Most amino acids have multiple codons. Reduces the impact of point mutations. |
| Non-overlapping | Bases are read in triplets (codons), each base used once. | Each base affects only one amino acid. |
| Universal | The same codons specify the same amino acids in almost all organisms. | Evidence for a common evolutionary ancestor. |
